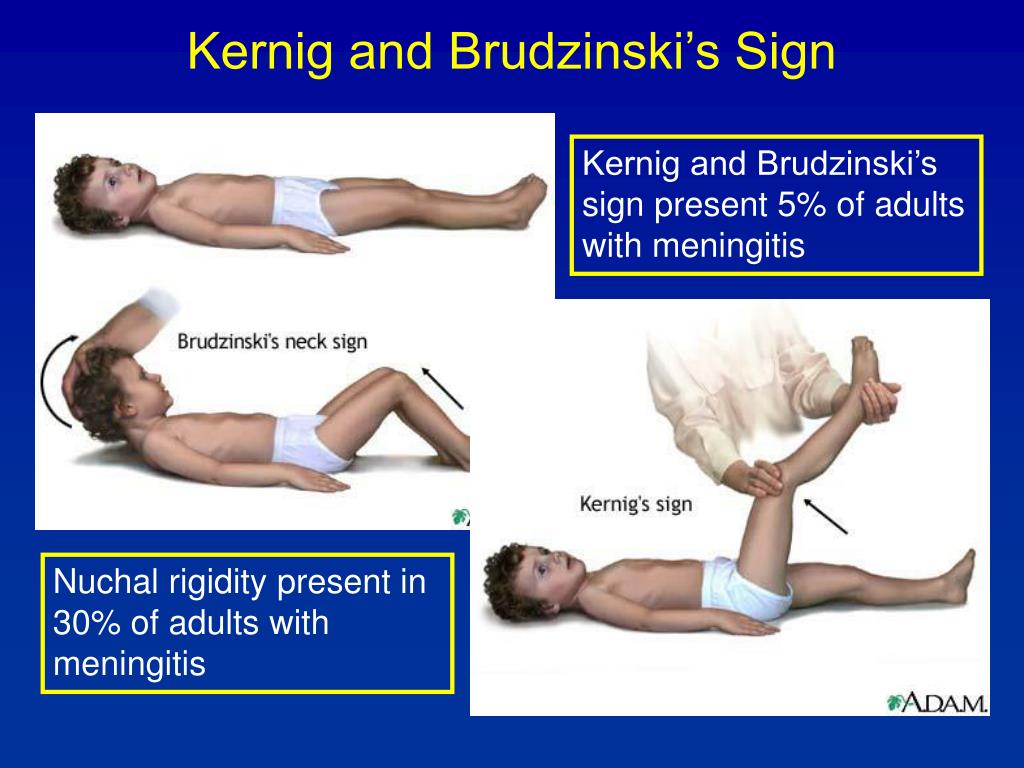
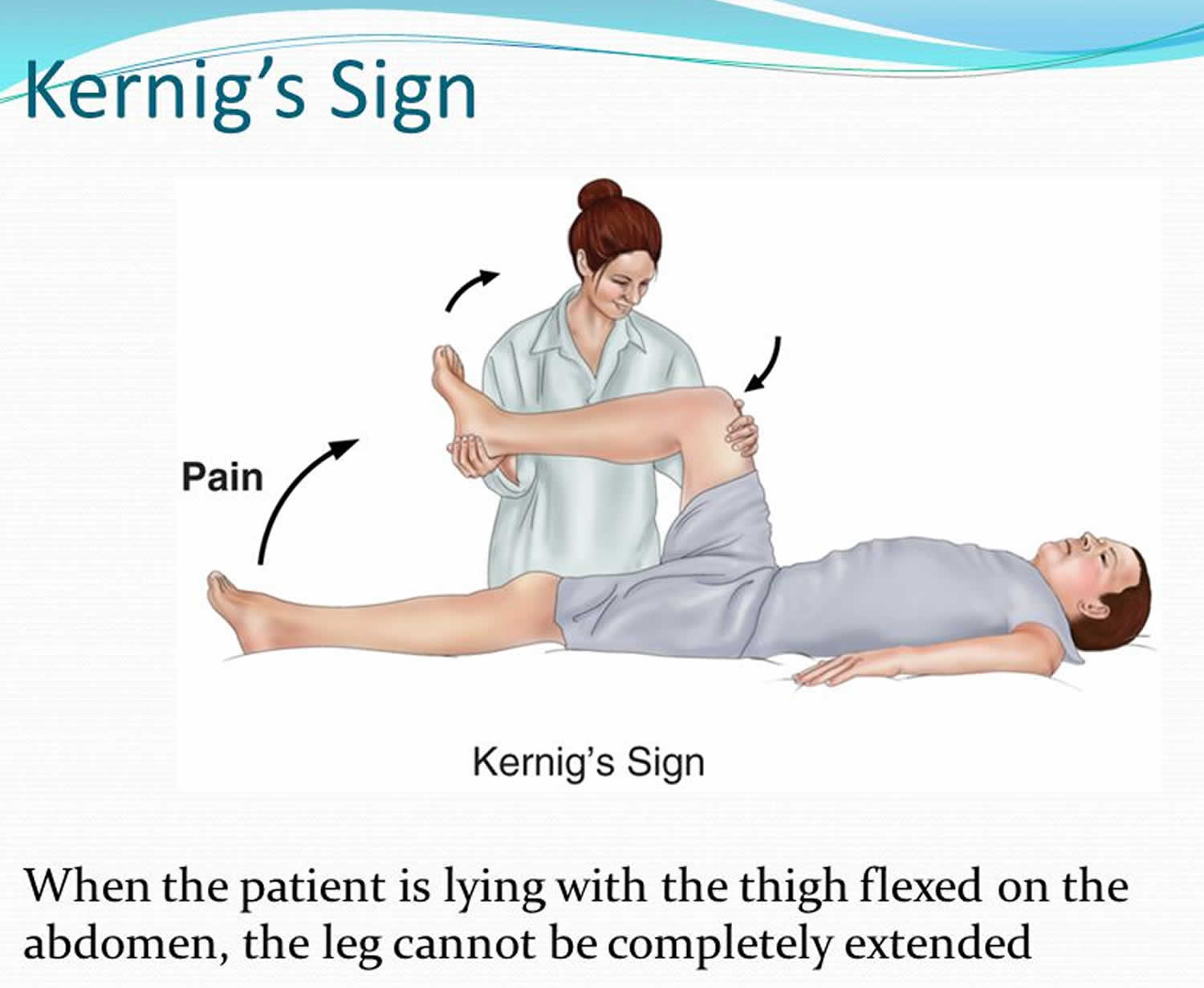
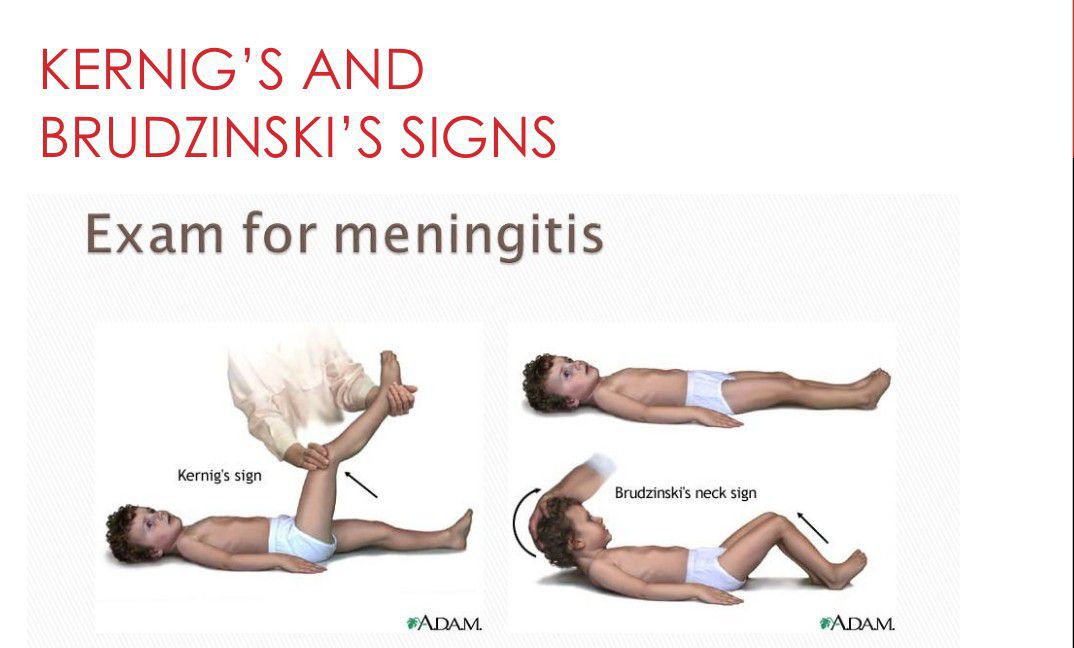
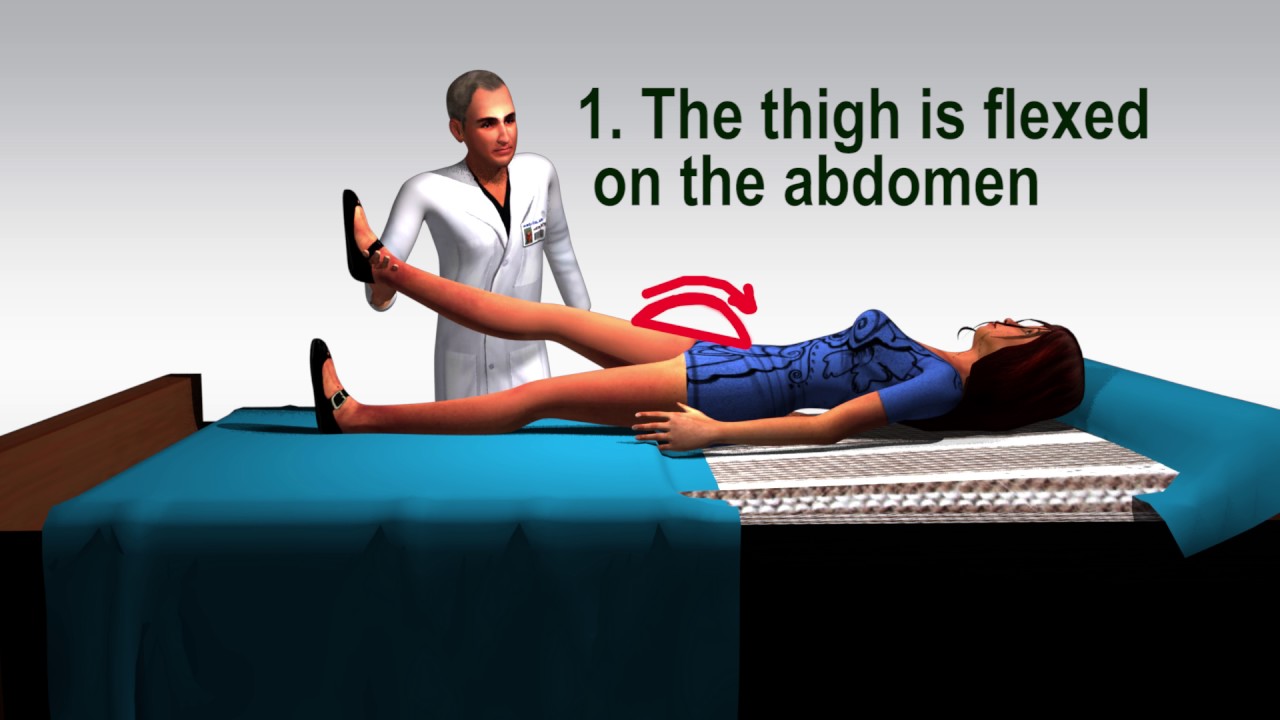
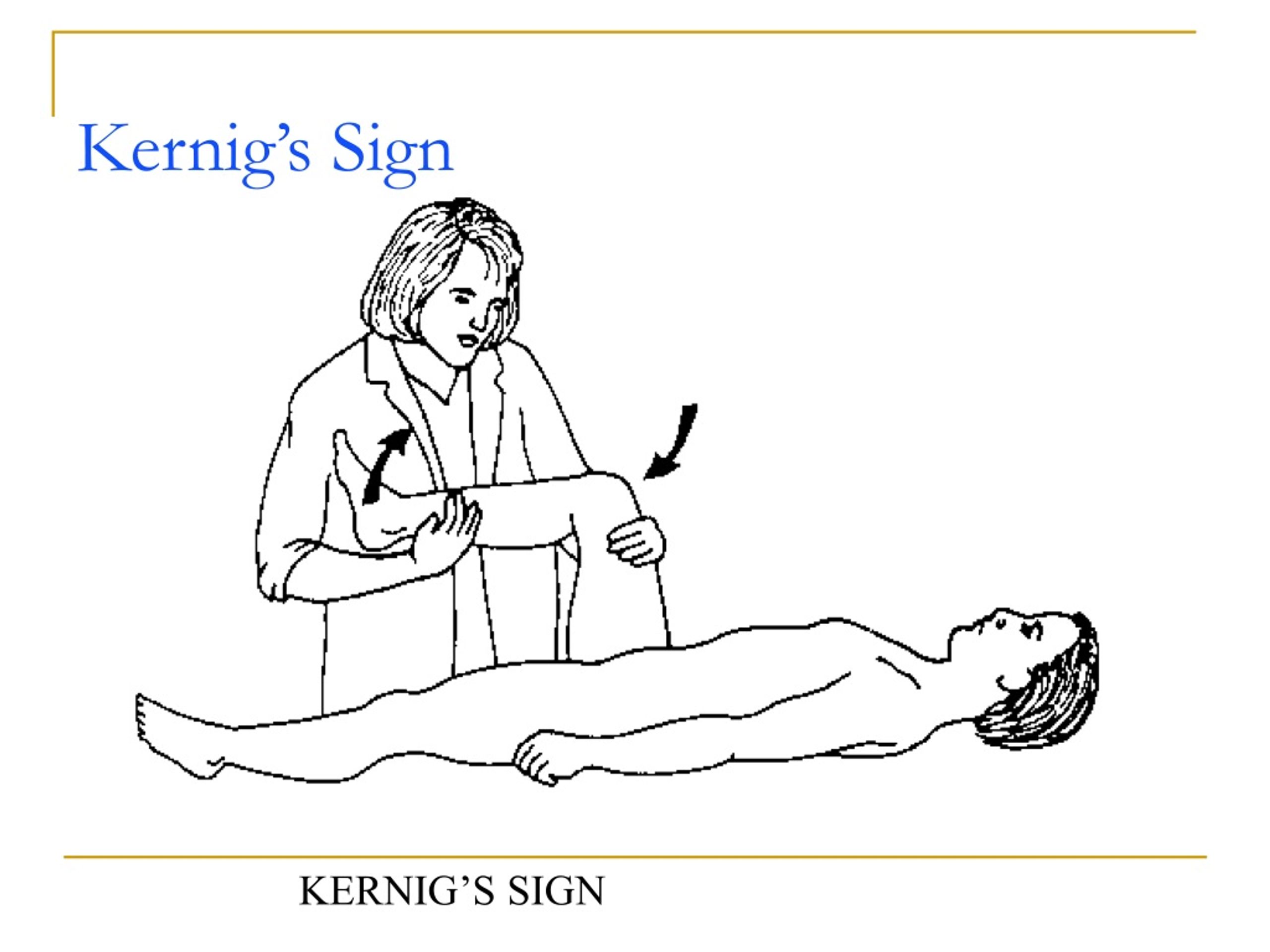
The specificity of jolt accentuation was 82%, Kernig sign was 97%, Brudzinski sign was 98%, and nuchal rigidity was 80%. Jolt accentuation in our cohort was poorly predictive of pleocytosis and insensitive. The presence of Kernig sign, Brudzinski sign, or nuchal rigidity has moderate positive but no negative predictive value for pleocytosis.. Early symptoms will be similar to the flu, and they can develop over a matter of hours or even days. Symptoms include: sudden high fever. stiff neck. severe headache. nausea or vomiting. confusion.
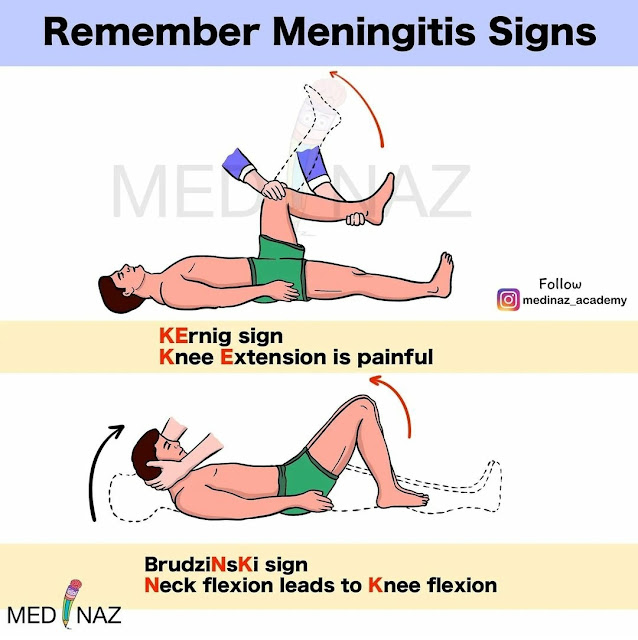
Kernig Sign and Brudzinski Sign Mnemonic
PPT Meningitis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4591726

Les Syndromes Méningés et Encéphaliques Dr Mohamed Zeroual YouTube
Kernig sign, Brudzinski sign, how to perform Kernig and Brudzinski test

Signo de Brudzinski (Terapeuta haz tu prueba funcional) Fisioterapia RD. (PF18) YouTube

Image result for kernig and brudzinski’s signs Kernig sign, Medical mnemonics, Medical school

Pin on Nervous System

Akute disseminierte Enzephalomyelitis (ADEM) ELearning mit Lecturio
Kernig sign, Brudzinski sign, how to perform Kernig and Brudzinski test

PPT SEMIOLOGIE DE L’ENFANT ET DU NOURRISSON (3) PowerPoint Presentation ID778086

Pin en medicina

How to pefrom the Kernig Sign for Meningitis YouTube

Kernig’s Sign YouTube
Kernig and Brudzinski Sign MEDizzy

meningitis
Kernig’s sign YouTube
PPT Unit 5 Meningitis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID604002
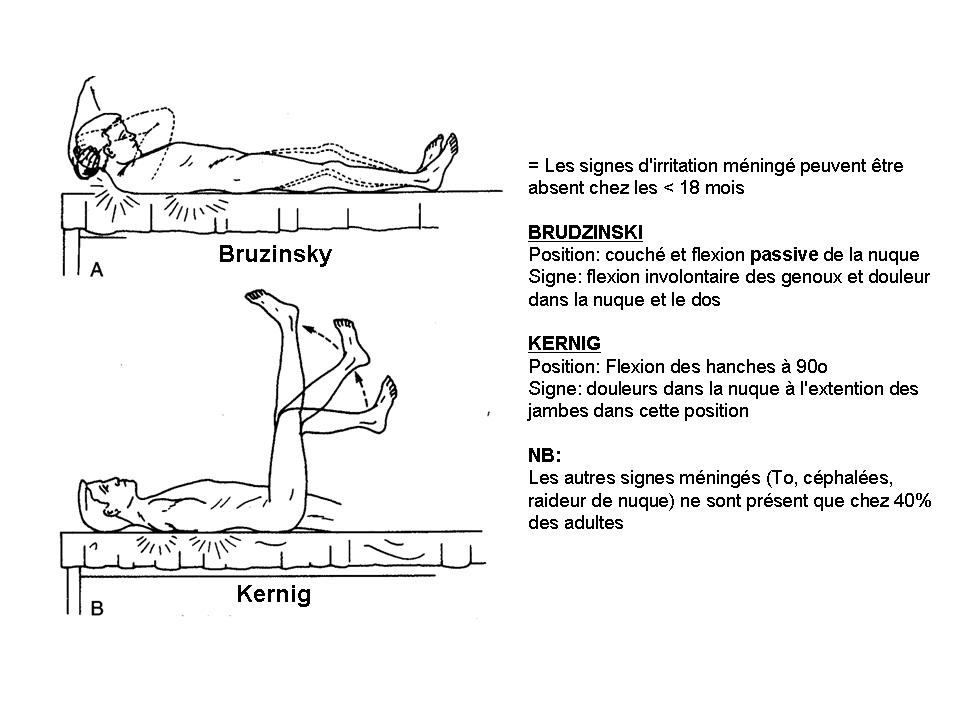
Index of /ENTREE/NEUROLOGIE

Brudzinski’s sign Meningitis sign YouTube

Signe de Brudzinski définition et lien avec la méningite
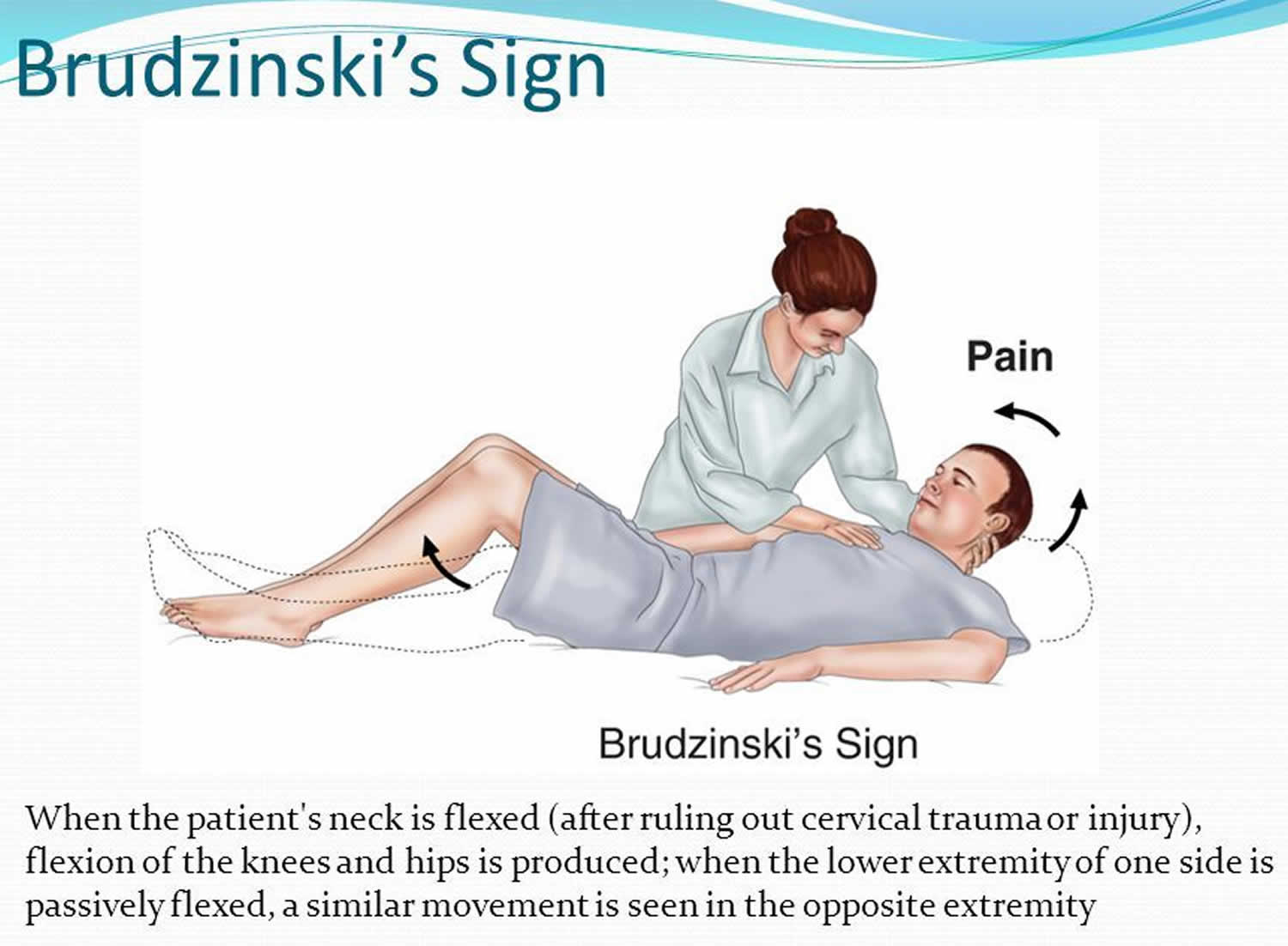
Brudzinski sign occurs in meningitis (of any etiology) or meningism where passive flexion of a patient’s neck elicits reflexive bilateral knee and hip flexion; it was originally known as the “nape of the neck sign” and was one of several physical exam maneuvers concurrently described to be characteristic of meningitis. Along with Kernig sign.. In 1909, Brudzinski reported that, for patients with bacterial or tuberculous meningitis, Kernig’s sign was 57% sensitive, and Brudzinski’s nape-of-the-neck sign was 96% sensitive . Since then, the presence of these clinical signs has been interpreted as evidence of meningeal inflammation.