Abstract. A detailed anatomic, histologic, and immunohistochemical study of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve (PCBMN) and its distal arborization was undertaken on 12 fresh human cadaveric hands. Small unmyelinated fibers terminated in the superficial loose connective tissue of the transverse carpal ligament.. A detailed anatomic, histologic, and immunohistochemical study of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve (PCBMN) and its distal arborization was undertaken on 12 fresh human cadaveric hands. Small unmyelinated fibers terminated in the superficial loose connective tissue of the transverse carpal ligament. There were no nerve fibers detected in the deep, dense collagen aspect of the.
Median Nerve Motor Branch My XXX Hot Girl
Median Nerve Wrist Anatomy
Ulnar Nerve Ulnar Nerve Hand Therapy Median Nerve Images and Photos finder
Volar Approach to Wrist Approaches Orthobullets

Tendon Diagram Hand Anatomy of the Hand and Wrist from the right hand. Points out many muscles

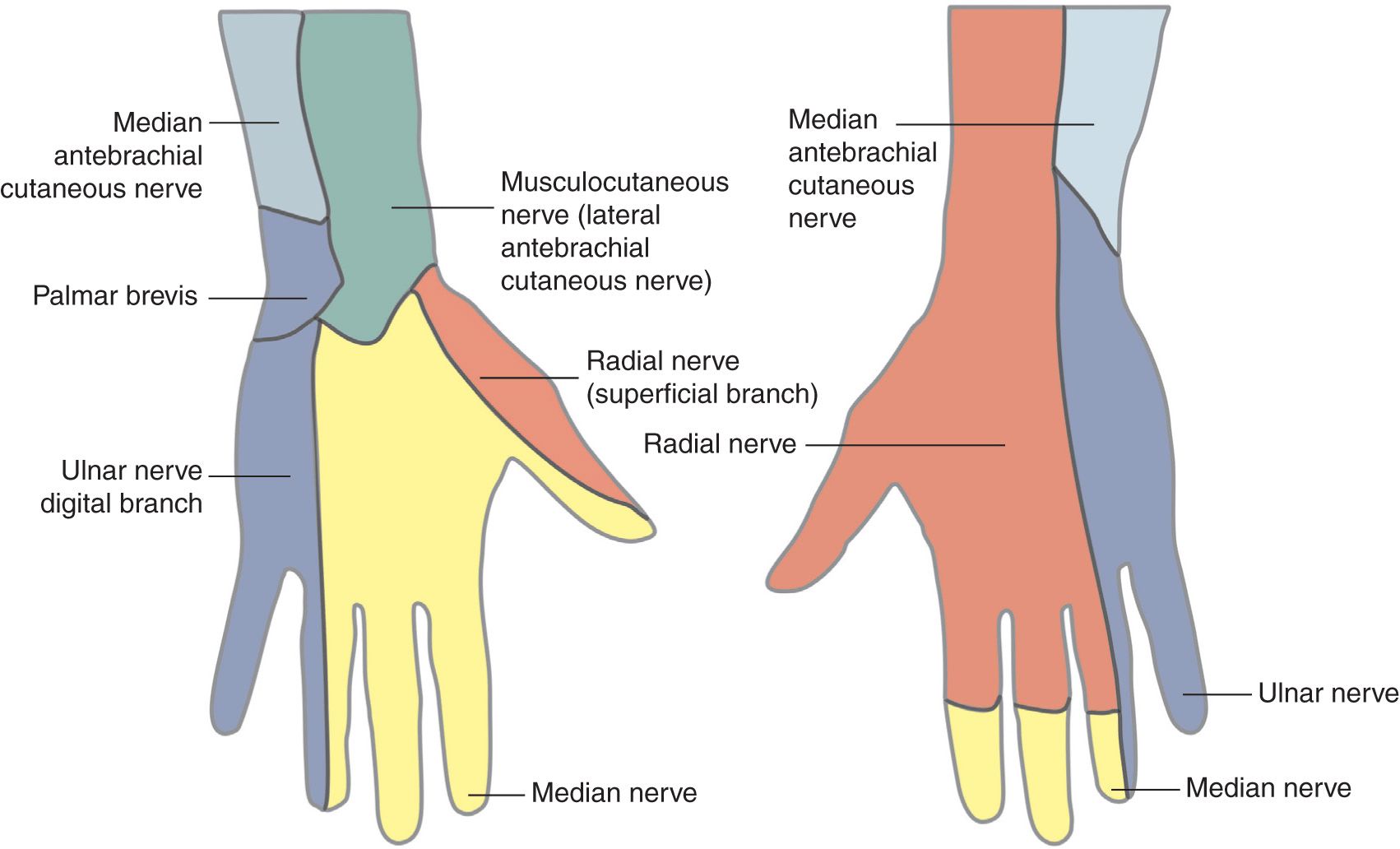
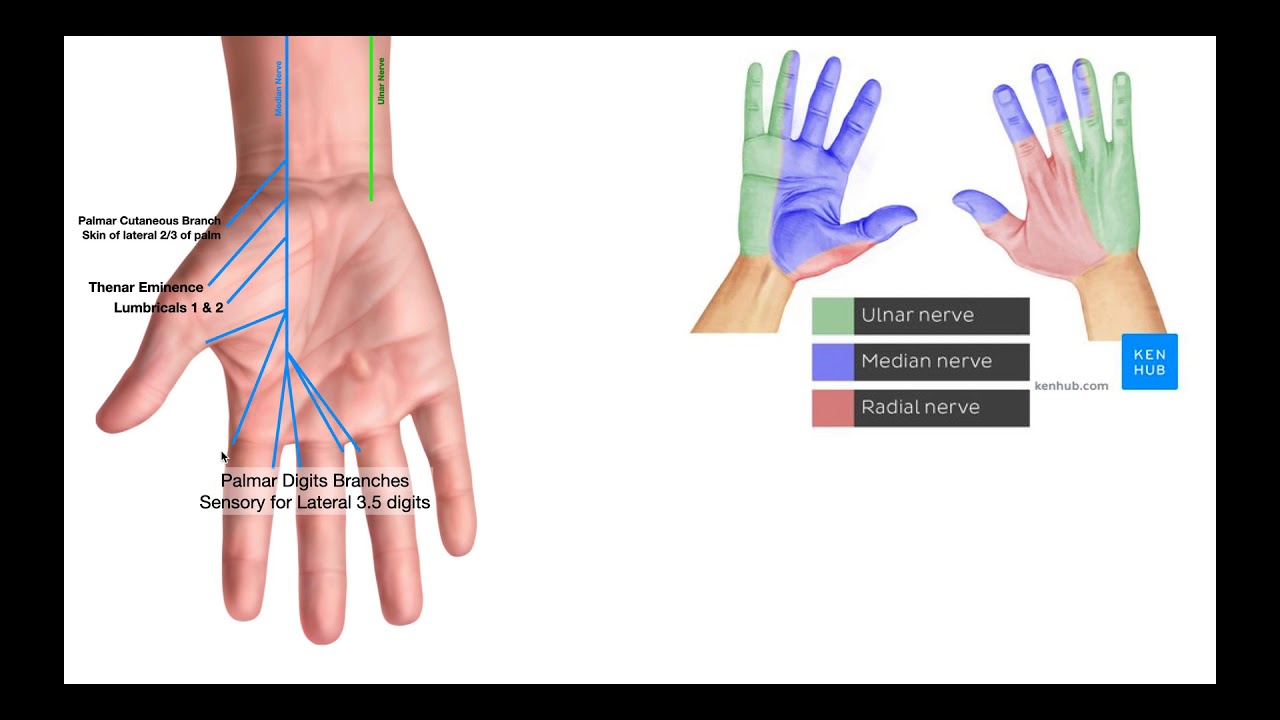
Cutaneous Innervation of Hand Diagram Quizlet

Navigating Naturopathy Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 101

Ulnar Nerve Innervation Hand Images and Photos finder
Branches of the Ulnar & Median Nerves [in Hand] YouTube
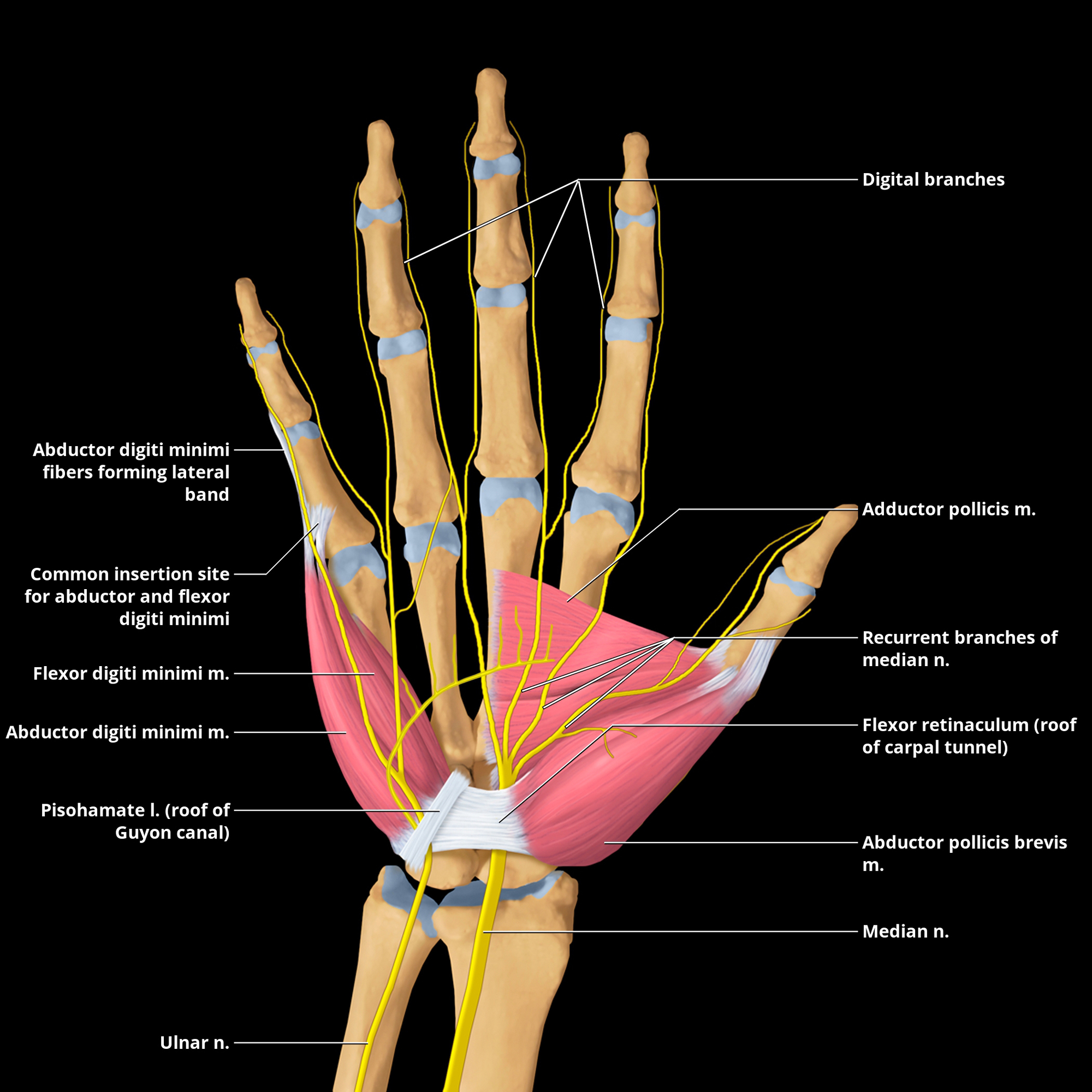
Median Nerve Radiology Key
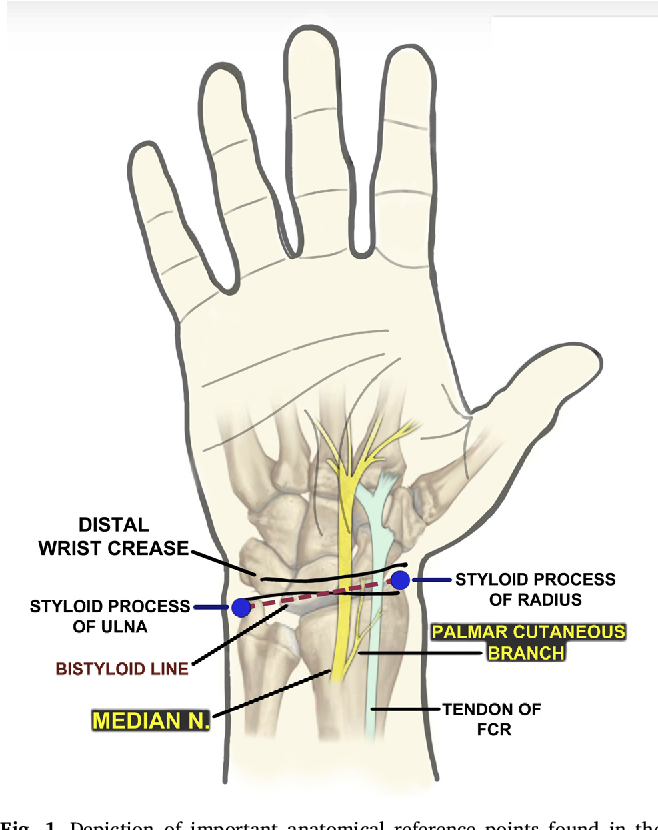
Figure 1 from Anatomy of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve A review. Semantic

Branches of median nerve below wrist Median nerve, Nerve anatomy, Nerve

Figure 1 from Anatomy of the palmar branch of the ulnar nerve application to ulnar and median

Pins and Needles From Fingers to Toes HighResolution MRI of Peripheral Sensory

Neuroanatomy Glossary Upper Limb Nerve Anatomy ditki medical & biological sciences

Volar Aspect

cutaneous innervation of hand Upper limb anatomy, Hands, Physical therapy
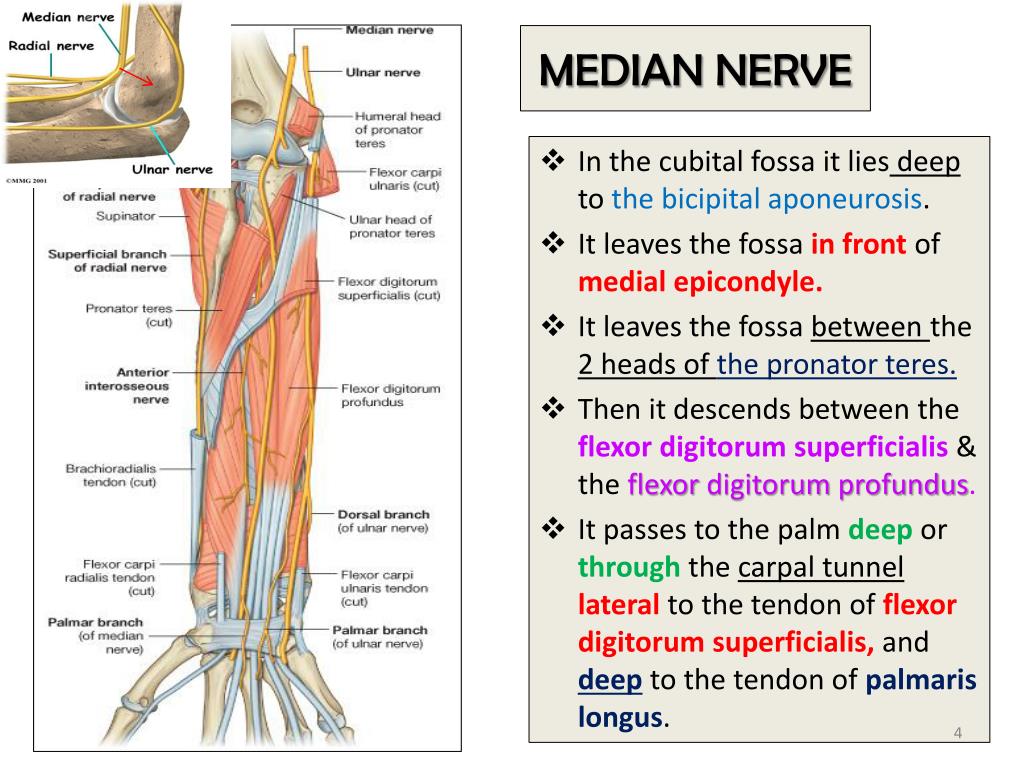
PPT MEDIAN & ULNAR NERVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1798439
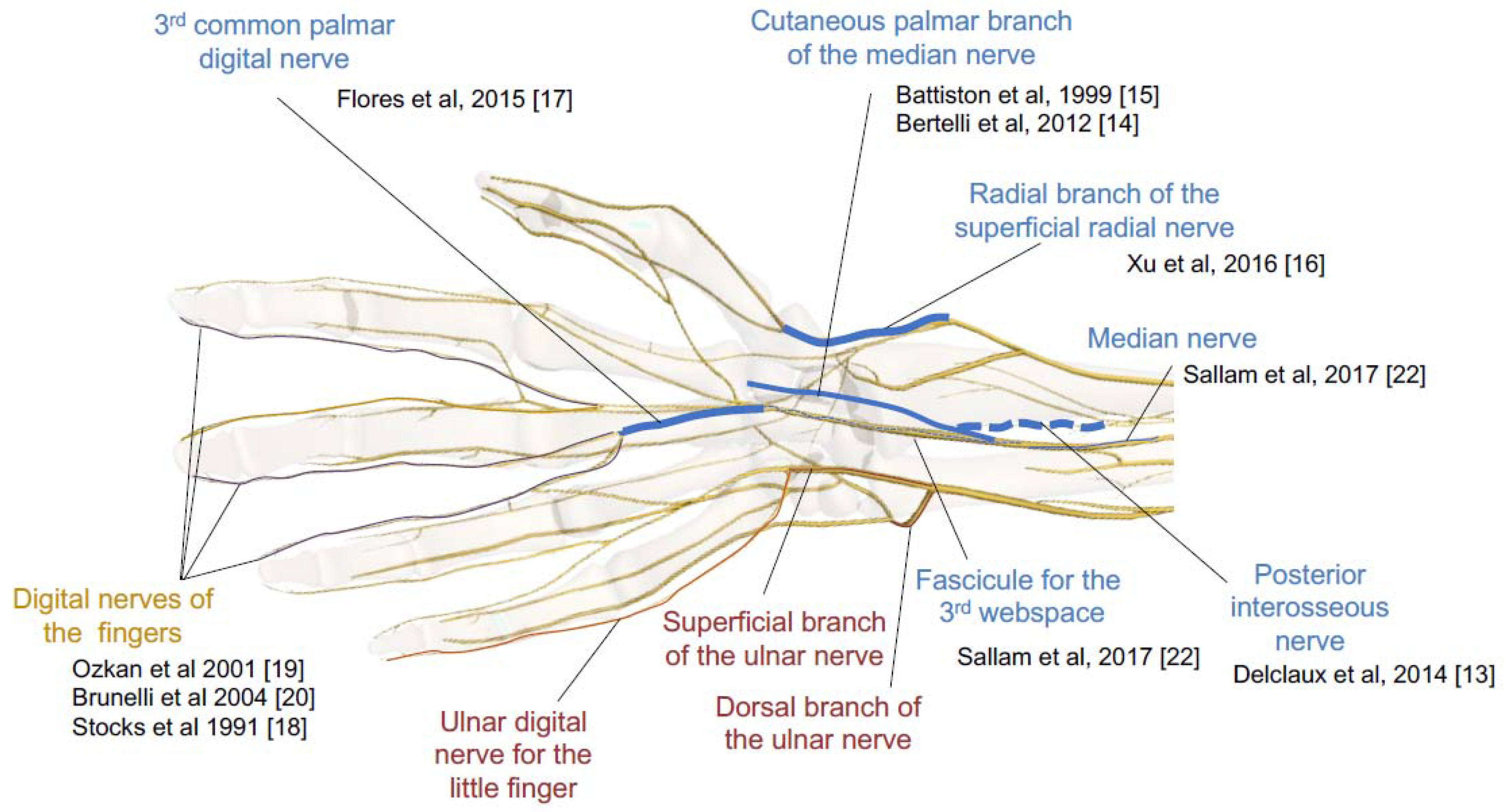
Ulnar Nerve Motor Branch Hot Sex Picture
PPT Nerves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4875596
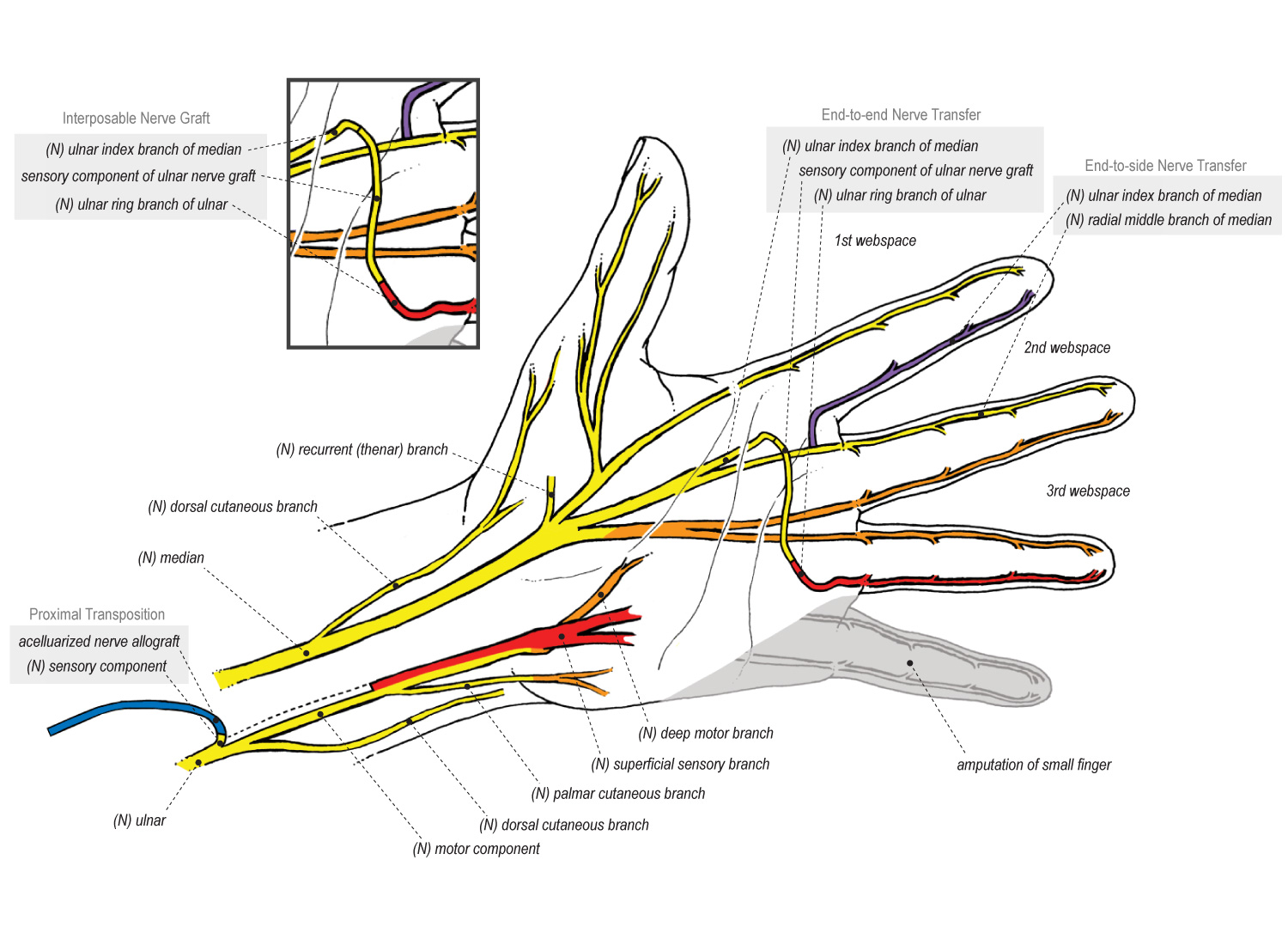
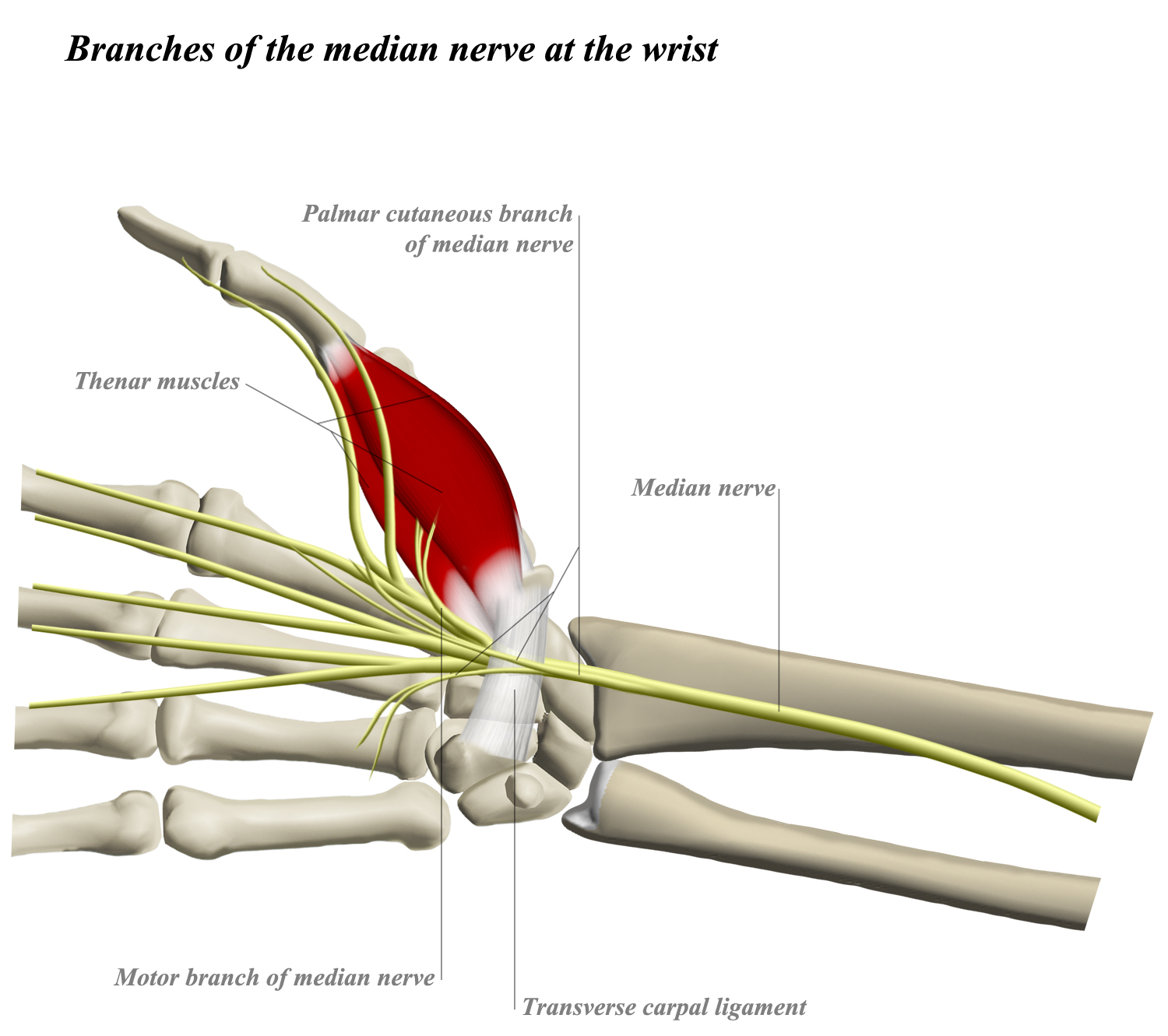
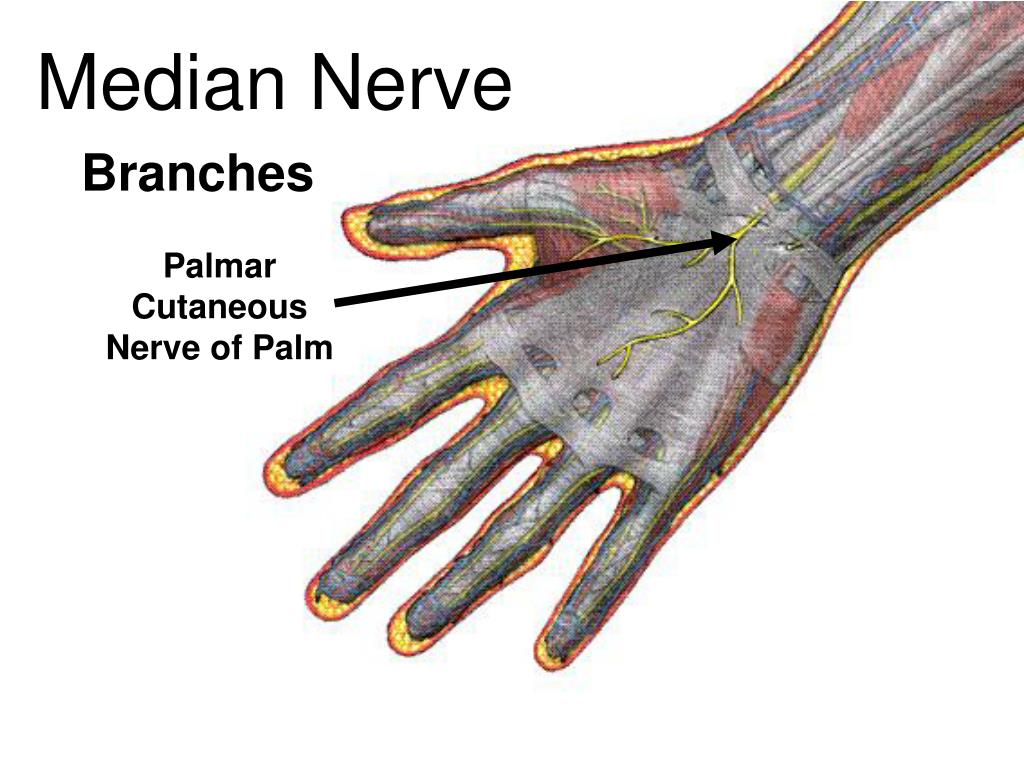
KEY WORDS: Hand/Innervation; Median nerve; Cadaver; Anatomy. INTRODUCTION The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve (PCBMN) origins from the medial margin of the median nerve (MN) 3 to 8 cm proximal to the wrist palmar crease. It remains connected to the MN for a few millimeters and thenceforward separates as a cutaneous branch, emerging. The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve (PCBm) is a constant structure. Only rarely has it been reported absent, such as in the study by Richards et al., where the nerve was nonexistent in two of twenty specimens. 1 This frequency is in agreement with a similar finding in Borne et al., in which the PCBm was present in 92% of limbs. 2.


